
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, act as legal, financial or credit advice. See Lexington Law’s editorial disclosure for more information.
While the house-hunting process is an exciting time in your life, it’s also crucial to consider the many factors that play into your mortgage application. Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is the metric lenders use to determine how much money you can borrow from them. If you have a high debt-to-income ratio, you may want to find ways to lower it to increase your approval odds.
But how do you calculate debt-to-income ratio, and what factors impact the formula?
We break down all aspects of calculating the DTI for mortgages and a few ways to lower your ratio to increase your chances of getting approved.
Key takeaways:
- Debt-to-income ratio for a mortgage represents the percentage of your monthly income spent on paying off debts, including mortgage payments, loans and credit card payments.
- Your front-end ratio focuses on housing-related expenses, including mortgage and home insurance payments.
- Your back-end ratio focuses on all monthly payments that go toward debt balances, including mortgage, credit cards, auto, etc.
- You can calculate your debt-to-income ratio for a mortgage by combining your monthly payments and dividing this amount by your gross monthly income.
Table of contents:
- What is debt-to-income ratio?
- Types of debt-to-income ratios
- How to calculate debt-to-income ratio
- What is a good debt-to-income ratio for a mortgage?
- Debt-to-income requirements by mortgage type
- How to lower your debt-to-income ratio
What is debt-to-income ratio?
Debt-to-income ratio represents the percentage of a person’s monthly income spent on paying off debt—this percentage factors in mortgage payments, rent, loans and credit card debt. Lenders might be concerned about working with someone with a high debt-to-income ratio due to the increased risk.
Types of debt-to-income ratios
Each lender can create their own standards and calculations when deciding whether someone is qualified for a loan. Your lender will choose which expenses to include in their required debt-to-income ratio for securing a mortgage. Front-end ratio and back-end ratio are the two most common calculations lenders use.
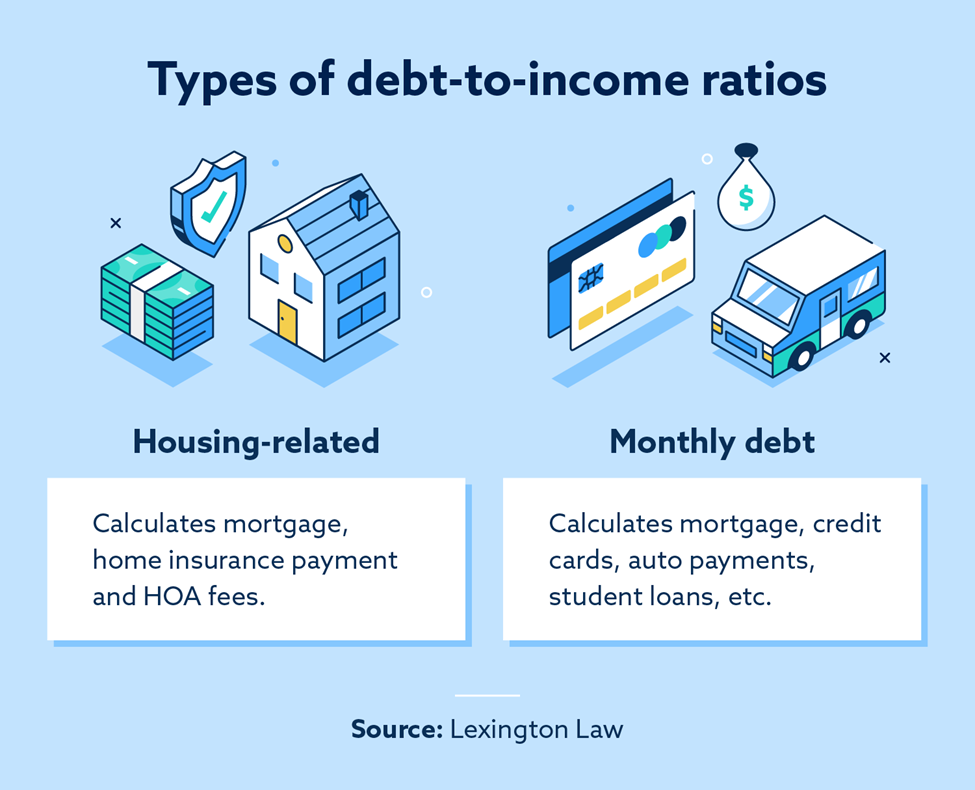
Front-end ratio
Front-end DTI ratio, also known as the housing ratio, combines all housing-related expenses, including mortgage and home insurance payments. The overall number shows the percentage of monthly income used for housing bills. Homeowners association dues and property taxes are also often included in this calculation.
Back-end ratio
Back-end DTI ratio combines your monthly debt payments, including your mortgage, credit cards, auto, student loans and so on. Lenders focus on this calculation more than the front-end ratio since it shows your spending habits and overall debt situation. This calculation does not include general living expenses like groceries or utilities.
How to calculate debt-to-income ratio
You can calculate your debt-to-income ratio by adding all your monthly payments and dividing by your gross monthly income.
You’ll want to factor in:
- All monthly house expenses
- Debt balances
- All loans
- Property taxes
- Any other regular and recurring payments
If you’re calculating your DTI with an additional applicant, make sure to combine both gross incomes and all debt and recurring payments.
Make sure to leave out the following items:
- Utilities
- Health insurance
- Groceries
- Gas and transportation
- Personal expenses
After you combine your monthly payments and divide this amount by your gross monthly income, you’ll want to convert this number to a percentage.
To convert your DTI to a percentage:
- Multiply the decimal result by 100
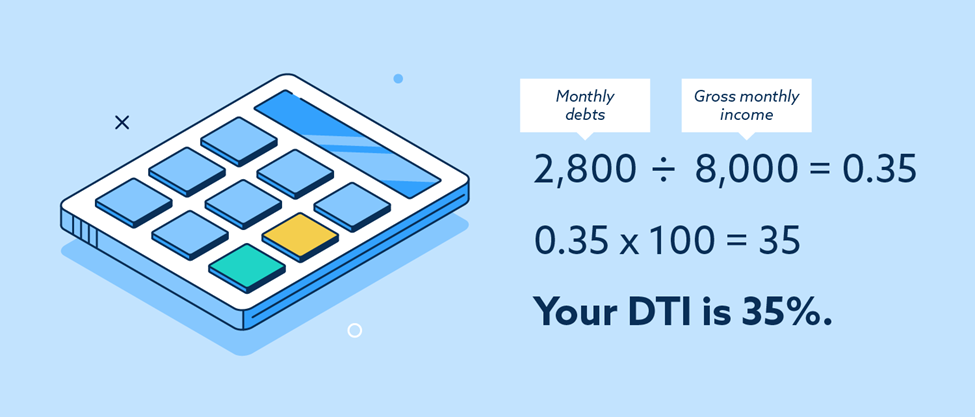
Debt-to-income ratio example
Using the debt-to-income ratio formula above, you can calculate your DTI. Let’s break down an example to show you the different steps if your monthly debt expenses add up to $2,800 and your gross monthly income is $8,000.
What is a good debt-to-income ratio for a mortgage?
According to Consumer Finance, a good debt-to-income ratio is below 43 percent for homeowners and below 20 percent for renters. However, lenders typically prefer for your DTI to be below 36 percent. The more room you have in your monthly budget can impress your lender and prove you can take on an additional loan payment while maintaining a balance for monthly expenses and emergencies.
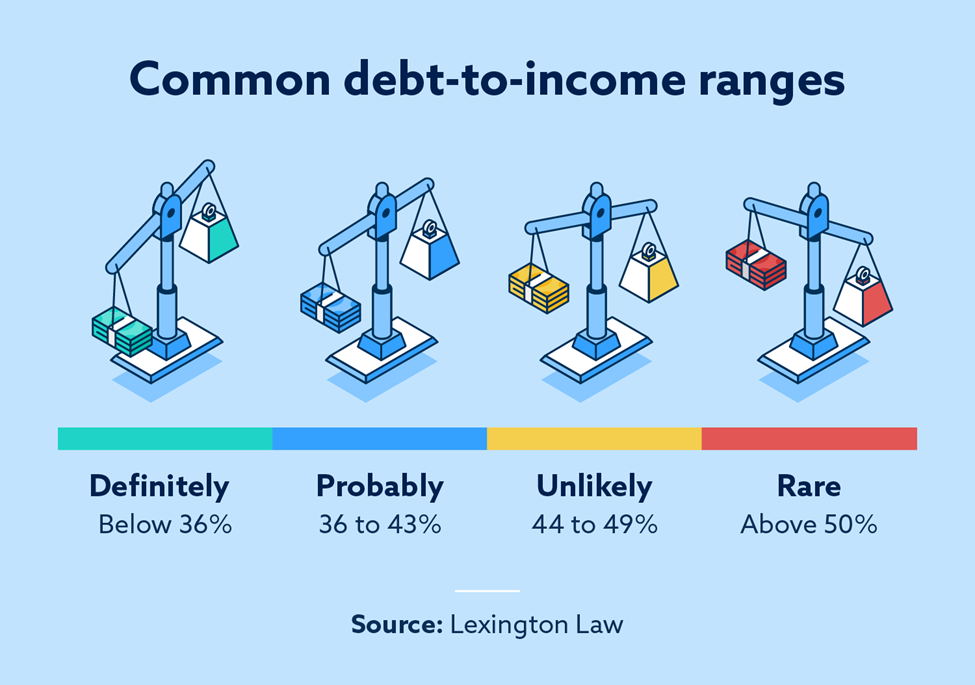
Here is a breakdown of common DTI ranges:
- 50 percent or more: Lower chance of being approved for a loan due to high debt levels.
- 44 to 49 percent: Reduces your approval rate since it shows a large amount of debt.
- 36 to 43 percent: Common DTI range for approving loan applicants.
- Below 36 percent: Highest chance of qualifying for a new loan or line of credit.
Debt-to-income requirements by mortgage type
It’s best to have a low debt-to-income ratio when applying for a mortgage. Every lender will require a different DTI. Here are the requirements for each type of mortgage.
FHA loans
FHA loans are provided by the U.S. Federal Housing Administration. You’ll need a 43 percent debt-to-income ratio for FHA loans, but some lenders may accept higher DTIs of up to 56.9 percent with compensating factors. These factors may include a high credit score or proof of steady employment. Keep in mind lenders will review your front-end DTI and back-end DTI.
USDA loans
USDA loans are backed by the government and designed for properties in rural areas. Applicants should have a DTI that doesn’t exceed 41 percent for this type of loan. Lenders will review the income of all household occupants, regardless if they are on the loan—this proves the household meets the income requirements. However, the lender will factor in the debts of only the people on the loan.
VA loans
VA loans come from the Department of Veterans Affairs, and they are more lenient regarding DTI requirements. This type of loan helps former military service members and their spouses purchase a home. The acceptable DTI for VA loans is 41 percent, but some lenders could approve you depending on additional factors.
How to lower your debt-to-income ratio
If your debt-to-income ratio for a mortgage is high, here are a few ways to lower it before applying for your loan.
Pay off your debts
A great way to improve your debt-to-income ratio is to pay off as much of your debt balance as possible. You can use the avalanche method, which involves paying off the debt with the highest interest rate first and working downward. The snowball method means you pay off the lowest balance first and work your way up your debt balance.
Increase your income
If you work additional hours or add a side hustle, you can help lower your DTI because you’re increasing your income. Remember that you’ll need to prove your income rate is consistent and will continue.
Use a cosigner
If you’re applying for a mortgage, adding an extra person to the application could increase your chances of getting approved. Your cosigner’s DTI will factor into the calculation, which can help increase your odds of getting a lower interest rate or a larger mortgage. The cosigner doesn’t need to live in your home, but they must agree to take on the payments if you can’t.
Debt-to-income ratio FAQ
Prepare for the mortgage application with these additional debt-to-income questions.
Are my debts calculated separately in my debt-to-income ratio?
Your debt-to-income ratio doesn’t weigh debts differently, and each type won’t affect your approval odds. DTI adds up all debt together, not separately. However, the more debt you have, the higher your DTI will be, which can hurt your chances of getting approved for a mortgage.
Can I improve my DTI fast?
You can improve your DTI by paying off your debt balance. Your chances of getting approved for a mortgage will also increase. A raise with your current employer or starting a side hustle can also help improve your DTI quickly.
Can I apply for a mortgage with a high DTI?
You can still apply for a mortgage with a high DTI, but the lender will likely offer you a higher interest rate. It’s best to lower your DTI ratio first to increase your chances of getting approved.
Does my DTI affect my credit score?
Your DTI doesn’t affect your credit score. Your DTI shows the percentage of your monthly income that goes toward paying your debt. DTI ratio and credit score are not correlated in any way. Debt-to-income ratio is one of the main things lenders review on your mortgage application. This financial metric illustrates your financial situation and shows if you can handle another loan on top of your debt. However, you may still qualify for a mortgage with a high DTI.
Learn how our credit repair services could help you work toward your financial goals today.
Note: Articles have only been reviewed by the indicated attorney, not written by them. The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, act as legal, financial or credit advice; instead, it is for general informational purposes only. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client or fiduciary relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website owner, authors, reviewers, contributors, contributing firms, or their respective agents or employers.
