
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, act as legal, financial or credit advice. See Lexington Law’s editorial disclosure for more information.
VantageScore® 3.0 is a credit scoring model that each of the three major credit bureaus uses to determine your creditworthiness.
VantageScore 3.0 is a popular credit scoring model that helps to reflect a person’s creditworthiness. VantageScore® and the FICO® score model help banks and lenders determine if they’ll offer credit cards and loans to applicants.
Understanding the factors that lower and raise your VantageScore can qualify you for better opportunities in the future. We’ll explain what VantageScore 3.0 is and how it works so you can work to improve your credit.
Table of contents:
- How does VantageScore 3.0 compare to other scoring models?
- How are Vantage credit scores calculated?
- 5 ways to improve your VantageScore 3.0
- Who is VantageScore 3.0 best for?
- How can I monitor my credit score?
How does VantageScore 3.0 compare to other scoring models?
VantageScore® 3.0 shares multiple similarities with other popular scoring models, including VantageScore 4.0 and several iterations of the FICO® scoring model.
There are also certain nuances that set each model apart when comparing VantageScore vs. FICO scoring models.
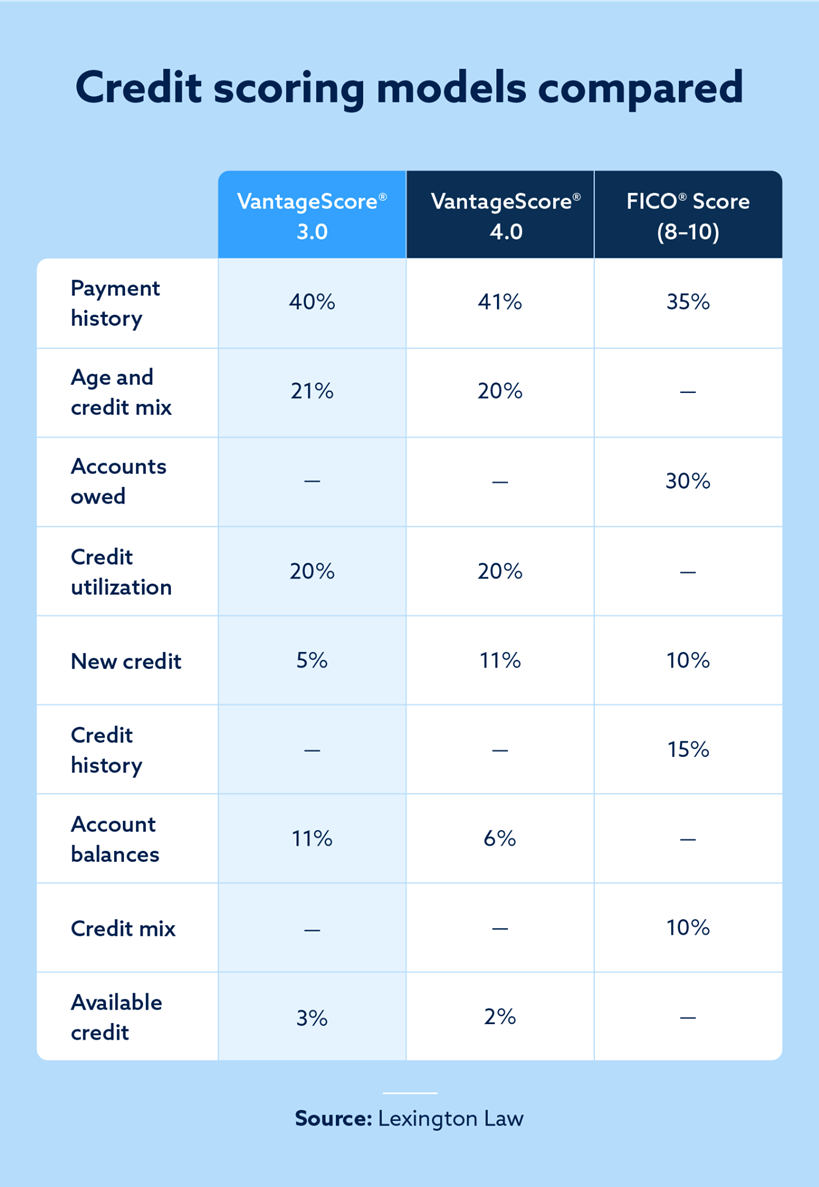
- VantageScore 3.0 and VantageScore 4.0 place a heavy emphasis on a person’s payment history, and they place a moderate emphasis on age and mix of credit and credit utilization rates. VantageScore 3.0 does focus more on a person’s total account balances, while VantageScore 4.0 is more concerned with new credit.
- FICO scores differ from VantageScore credit scores in several ways. FICO scores need six months of account activity to generate credit scores, while VantageScore credit scores just need one. VantageScore credit scores generally take six categories into account, while FICO scores focus on 5. Otherwise, VantageScore credit scores and FICO scores both use 300 to 850 credit ranges — and the factors they use to calculate credit scores are generally similar.
How is VantageScore 3.0 calculated?
If you’ve ever asked yourself, “Why are my credit scores different?” learning how a VantageScore 3.0 is calculated may provide clarity.
- Payment history makes up roughly 40 percent of your VantageScore and can significantly increase or decrease your score based on how timely you are with your payments.
- The age of your credit and how diverse your credit profile make up about 21 percent of your VantageScore. If you have a wide range of account types and consistently make on-time payments with your oldest accounts, your VantageScore will likely steadily improve.
- Credit utilization composes 20 percent of your VantageScore. Your credit utilization ratio is determined by weighing how much of your available credit you’re currently using.
- Your brand-new credit accounts only make up five percent of your VantageScore.
- The total amount of your account balances contributes roughly 11 percent to your VantageScore. This factor is also linked to your credit utilization ratio.
- Available credit makes up about three percent of your VantageScore and generally reflects how much credit you’ve taken out.
The answer to “When do credit scores update?” is a bit complex. Credit scores are frequently updated, but there’s no preset date for these updates. It’s best to regularly check your credit scores and dispute any errors that you notice.
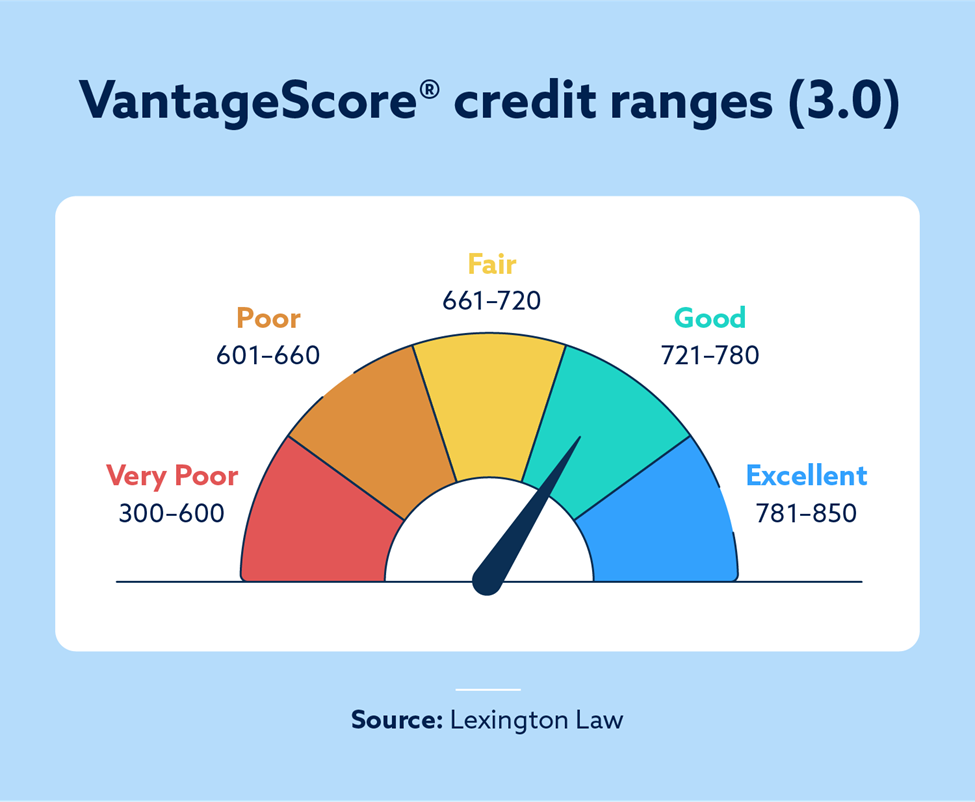
VantageScore 3.0 credit ranges
Just like a FICO credit score, VantageScore credit scores can fall between 300 and 850. However, there are subtle differences between the credit score ranges of both models. For example, a FICO credit score of 780 would be considered “very good,” while a VantageScore 3.0 credit score of 780 is simply considered “good.”
Here’s a full breakdown of the VantageScore 3.0 credit score ranges:
- Very poor: 300 – 600
- Poor: 601 – 660
- Fair: 661 – 720
- Good: 721 – 780
- Excellent: 781 – 850
5 ways to improve your VantageScore 3.0
Consistently practicing good financial habits can improve your VantageScore over time. The following tips can help you work on poor credit and eventually reach and maintain higher scores.
1. Don’t apply for too much new credit
Each time you apply for credit, creditors will enact a hard inquiry on your account that temporarily lowers your score. If you apply for too much new credit within a set period, your credit score may sharply decline.
2. Pay down credit card balances
Account balances compose 11 percent of your VantageScore, so paying down your debt can positively impact your credit. Lowering your account balances will also improve your credit utilization ratio, especially if you target your largest balances first.
3. Try to make your payments on time
Since payment history makes up 40 percent of your VantageScore, this step’s importance can’t be understated. Strive to make all of your payments on time. Even if you can only make the minimum payment or have to pay within the grace period, you’ll still maintain good standing with your creditors.
4. Maintain your oldest accounts
Taking positive actions on your oldest accounts will have a greater impact than activity on your newer accounts. Remember that merging your oldest accounts can drastically lower your score if you ever consider using a debt consolidation service.
5. Sign up for a credit monitoring service
A credit monitoring service can monitor your credit reports and clue you into any fluctuations or inconsistencies. Lexington Law Firm offers comprehensive credit monitoring services that can help you take positive steps toward improving your credit.
Who is VantageScore 3.0 best for?
While VantageScore 3.0 is a valuable credit scoring model for a wide range of people, it’s particularly beneficial if you have any of the following:
- Limited credit history: VantageScore 3.0 can be helpful if you’re just starting to build your credit history, as it considers a broader range of data, including rent payments and utility bills.
- Recent credit issues: If you’ve had recent financial setbacks, such as late payments or defaults, VantageScore 3.0 can provide a more forgiving assessment of your creditworthiness compared to other scoring models.
- A diverse credit profile: If you have a mix of credit accounts, including credit cards, mortgages and auto loans, VantageScore 3.0 can provide a more accurate picture of your overall credit health compared to scoring models that more heavily weigh certain types of credit, like credit cards.
How can I monitor my credit score?
Monitoring your credit score is a crucial step in maintaining your financial health. By closely monitoring your credit report and score, you can identify potential issues early on, like errors or fraudulent activity.
With regular monitoring, you can take proactive steps to improve your creditworthiness to ensure that you’re getting the best possible interest rates on loans and credit cards.
You can monitor your credit by reaching out to the three credit bureaus and requesting a free credit report. You can also capitalize on credit monitoring services like the products offered by Lexington Law Firm. Get your free credit assessment today.
VantageScore 3.0 FAQ
Do banks use FICO or VantageScore?
Many banks use both FICO and VantageScore to assess someone’s creditworthiness. The specific scoring model they use will vary by bank or lender and can also depend on the type of loan or credit product you’re applying for.
How often is my VantageScore updated?
Your VantageScore can be updated multiple times per month. However, the frequency of updates can vary depending on changes in your credit report.
Can I check my VantageScore for free?
While you can’t directly check your VantageScore for free, many credit monitoring services and financial institutions offer access to your VantageScore as part of their services.
What is the difference between a VantageScore and a FICO score?
While both FICO and VantageScore are credit scoring models, they use slightly different algorithms and data to calculate your creditworthiness.
FICO scores require a minimum of six months of credit history to generate a score, whereas VantageScore credit scores can be calculated with as little as one month of activity. Additionally, VantageScore scoring models consider six categories of credit information, while FICO scores primarily focus on five.
Which score do lenders typically use?
Lenders typically use both FICO and VantageScore to make credit decisions. The specific score they prioritize may depend on the type of loan or credit product you’re applying for.
Note: Articles have only been reviewed by the indicated attorney, not written by them. The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, act as legal, financial or credit advice; instead, it is for general informational purposes only. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client or fiduciary relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website owner, authors, reviewers, contributors, contributing firms, or their respective agents or employers.
